微信小程序中页面间通信的方式
PageModel(页面模型)对小程序而言是很重要的一个概念,从app.json中也可以看到,小程序就是由一个个页面组成的。
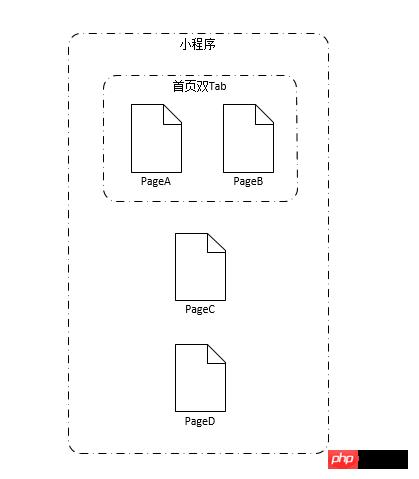
如上图,这是一个常见结构的小程序:首页是一个双Tab框架PageA和PageB,子页面pageB, PageC。
让我们假设这样一个场景:首页PageA有一个飘数,当我们从PageA新开PageC后,做一些操作,再回退到PageA的时候,这个飘数要刷新。很显然,这需要在PageC中做操作时,能通知到PageA,以便PageA做相应的联动变化。
这里的通知,专业点说就是页面通信。所谓通信,u3认为要满足下面两个条件:
激活对方的一个方法调用
能够向被激活的方法传递数据
本文将根据项目实践,结合小程序自身特点,就小程序页面间通信方式作一个探讨与小结。
通信分类
按页面层级(或展示路径)可以分为:
兄弟页面间通信。如多Tab页面间通信,PageA,PageB之间通信
父路径页面向子路径页面通信,如PageA向PageC通信
子路径页面向父路径页面通信,如PageC向PageA通信
按通信时激活对方方法时机,又可以分为:
延迟激活,即我在PageC做完操作,等返回到PageA再激活PageA的方法调用
立即激活,即我在PageC做完操作,在PageC激活PageA的方法调用
方式一:onShow/onHide + localStorage
利用onShow/onHide激活方法,通过localStorage传递数据。大概逻辑如下
// pageA
let isInitSelfShow = true;
Page({
data: {
helloMsg: 'hello from PageA'
},
onShow() {
// 页面初始化也会触发onShow,这种情况可能不需要检查通信
if (isInitSelfShow) return;
let newHello = wx.getStorageSync('__data');
if (newHello) {
this.setData({
helloMsg: newHello
});
// 清队上次通信数据
wx.clearStorageSync('__data');
}
},
onHide() {
isInitSelfShow = false;
},
goC() {
wx.navigateTo({
url: '/pages/c/c'
});
}
});// pageC
Page({
doSomething() {
wx.setStorageSync('__data', 'hello from PageC');
}
});